Category Archives: Interview
(Model view controller)MVC Interview questions and answers
Disclaimer
What is MVC(Model view controller)?
Can you explain the complete flow of MVC?
Is MVC suitable for both windows and web application?
What are the benefits of using MVC?
Is MVC different from a 3 layered architecture?
What is the latest version of MVC?
What is the difference between each version of MVC?
What are routing in MVC?
Where is the route mapping code written?
Can we map multiple URL’s to the same action?
How can we navigate from one view to other view using hyperlink?
How can we restrict MVC actions to be invoked only by GET or POST?
How can we maintain session in MVC?
What is the difference between tempdata,viewdata and viewbag?
What are partial views in MVC?
How did you create partial view and consume the same?
How can we do validations in MVC?
Can we display all errors in one go?
How can we enable data annotation validation on client side?
What is razor in MVC?
Why razor when we already had ASPX?
So which is a better fit Razor or ASPX?
How can you do authentication and authorization in MVC?
How to implement windows authentication for MVC?
How do you implement forms authentication in MVC?
How to implement Ajax in MVC?
What kind of events can be tracked in AJAX?
What is the difference between “ActionResult” and “ViewResult”?
What are the different types of results in MVC?
What are “ActionFilters”in MVC?
Can we create our custom view engine using MVC?
How to send result back in JSON format in MVC?
What is “WebAPI”?
But WCF SOAP also does the same thing, so how does “WebAPI” differ?
With WCF also you can implement REST,So why “WebAPI”?
Disclaimer
By reading these MVC interview question it does not mean you will go and clear MVC interviews. The whole purpose of this article is to quickly brush up your MVC knowledge before you for the MVC interviews.
This article does not teach MVC, it’s a last minute revision sheet before going for MVC interviews.
In case you want to learn MVC from scratch start by reading Learn MVC ( Model view controller) step by step 7 days or you can also start with my step by step MVC ( Model view controller) video series from youtube.
What is MVC(Model view controller)?
MVC is architectural pattern which separates the representation and the user interaction. It’s divided in three broader sections, “Model”, “View” and “Controller”. Below is how each one of them handles the task.
- The “View” is responsible for look and feel.
- “Model” represents the real world object and provides data to the “View”.
- The “Controller” is responsible to take the end user request and load the appropriate “Model” and “View”.
Figure: – MVC (Model view controller)
Can you explain the complete flow of MVC?
Below are the steps how control flows in MVC (Model, view and controller) architecture:-
- All end user requests are first sent to the controller.
- The controller depending on the request decides which model to load. The controller loads the model and attaches the model with the appropriate view.
- The final view is then attached with the model data and sent as a response to the end user on the browser.
Is MVC suitable for both windows and web application?
MVC architecture is suited for web application than windows. For window application MVP i.e. “Model view presenter” is more applicable.IfyouareusingWPFandSLMVVMismoresuitableduetobindings.
What are the benefits of using MVC?
There are two big benefits of MVC:-
Separation of concerns is achieved as we are moving the code behind to a separate class file. By moving the binding code to a separate class file we can reuse the code to a great extent.
Automated UI testing is possible because now the behind code (UI interaction code) has moved to a simple.NET class. This gives us opportunity to write unit tests and automate manual testing.
Is MVC different from a 3 layered architecture?
MVC is an evolution of a 3 layered traditional architecture. Many components of 3 layered architecture are part of MVC. So below is how the mapping goes.
| Functionality | 3 layered / tiered architecture | Model view controller architecture |
| Look and Feel | User interface. | View. |
| UI logic | User interface. | Controller |
| Business logic /validations | Middle layer | Model. |
| Request is first sent to | User interface | Controller. |
| Accessing data | Data access layer. | Data access layer. |
Figure: – 3 layered architecture
What is the latest version of MVC?
When this note was written, four versions where released of MVC. MVC 1 , MVC 2, MVC 3 and MVC 4. So the latest is MVC 4.
What is the difference between each version of MVC?
Below is a detail table of differences. But during interview it’s difficult to talk about all of them due to time limitation. So I have highlighted important differences which you can run through before the interviewer.
| MVC 2 | MVC 3 | MVC 4 |
| Client-Side Validation Templated Helpers Areas Asynchronous Controllers Html.ValidationSummary Helper Method DefaultValueAttribute in Action-Method Parameters Binding Binary Data with Model Binders DataAnnotations Attributes Model-Validator Providers New RequireHttpsAttribute Action Filter Templated Helpers Display Model-Level Errors | RazorReadymade project templatesHTML 5 enabled templatesSupport for Multiple View EnginesJavaScript and AjaxModel Validation Improvements | ASP.NET Web APIRefreshed and modernized default project templatesNew mobile project templateMany new features to support mobile apps Enhanced support for asynchronous methods |
What are routing in MVC?
Routing helps you to define a URL structure and map the URL with the controller.
For instance let’s say we want that when any user types “http://localhost/View/ViewCustomer/”, it goes to the “Customer” Controller and invokes “DisplayCustomer” action. This is defined by adding an entry in to the “routes” collection using the “maproute” function. Below is the under lined code which shows how the URL structure and mapping with controller and action is defined.
routes.MapRoute(
"View", // Route name
"View/ViewCustomer/{id}", // URL with parameters
new { controller = "Customer", action = "DisplayCustomer",
id = UrlParameter.Optional }); // Parameter defaults
Where is the route mapping code written?
The route mapping code is written in the “global.asax” file.
Can we map multiple URL’s to the same action?
Yes , you can , you just need to make two entries with different key names and specify the same controller and action.
How can we navigate from one view to other view using hyperlink?
By using “ActionLink” method as shown in the below code. The below code will create a simple URL which help to navigate to the “Home” controller and invoke the “GotoHome” action.
<%= Html.ActionLink("Home","Gotohome") %>
How can we restrict MVC actions to be invoked only by GET or POST?
We can decorate the MVC action by “HttpGet” or “HttpPost” attribute to restrict the type of HTTP calls. For instance you can see in the below code snippet the “DisplayCustomer” action can only be invoked by “HttpGet”. If we try to make Http post on “DisplayCustomer” it will throw an error.
[HttpGet]
public ViewResult DisplayCustomer(int id)
{
Customer objCustomer = Customers[id];
return View("DisplayCustomer",objCustomer);
}
How can we maintain session in MVC?
Sessions can be maintained in MVC by 3 ways tempdata ,viewdata and viewbag.
What is the difference between tempdata ,viewdata and viewbag?
Figure:- difference between tempdata , viewdata and viewbag
Temp data: –Helps to maintain data when you move from one controller to other controller or from one action to other action. In other words when you redirect,“tempdata” helps to maintain data between those redirects. It internally uses session variables.
View data: – Helps to maintain data when you move from controller to view.
View Bag: – It’s a dynamic wrapper around view data. When you use “Viewbag” type casting is not required. It uses the dynamic keyword internally.
Figure:-dynamic keyword
Session variables: – By using session variables we can maintain data from any entity to any entity.
Hidden fields and HTML controls: – Helps to maintain data from UI to controller only. So you can send data from HTML controls or hidden fields to the controller using POST or GET HTTP methods.
Below is a summary table which shows different mechanism of persistence.
| Maintains data between | ViewData/ViewBag | TempData | Hidden fields | Session |
| Controller to Controller | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| Controller to View | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| View to Controller | No | No | Yes | Yes |
What are partial views in MVC?
Partial view is a reusable view (like a user control) which can be embedded inside other view. For example let’s say all your pages of your site have a standard structure with left menu, header and footer as shown in the image below.
Figure:- partial views in MVC
For every page you would like to reuse the left menu, header and footer controls. So you can go and create partial views for each of these items and then you call that partial view in the main view.
How did you create partial view and consume the same?
When you add a view to your project you need to check the “Create partial view” check box.
Figure:-createpartialview
Once the partial view is created you can then call the partial view in the main view using “Html.RenderPartial” method as shown in the below code snippet.
<body>
<div>
<% Html.RenderPartial("MyView"); %>
</div>
</body>
How can we do validations in MVC?
One of the easy ways of doing validation in MVC is by using data annotations. Data annotations are nothing but attributes which you can be applied on the model properties. For example in the below code snippet we have a simple “customer” class with a property “customercode”.
This”CustomerCode” property is tagged with a “Required” data annotation attribute. In other words if this model is not provided customer code it will not accept the same.
public class Customer
{
[Required(ErrorMessage="Customer code is required")]
public string CustomerCode
{
set;
get;
}
}
In order to display the validation error message we need to use “ValidateMessageFor” method which belongs to the “Html” helper class.
<% using (Html.BeginForm("PostCustomer", "Home", FormMethod.Post))
{ %>
<%=Html.TextBoxFor(m => m.CustomerCode)%>
<%=Html.ValidationMessageFor(m => m.CustomerCode)%>
<input type="submit" value="Submit customer data" />
<%}%>
Later in the controller we can check if the model is proper or not by using “ModelState.IsValid” property and accordingly we can take actions.
public ActionResult PostCustomer(Customer obj)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
obj.Save();
return View("Thanks");
}
else
{
return View("Customer");
}
}
Below is a simple view of how the error message is displayed on the view.
Figure:- validations in MVC
Can we display all errors in one go?
Yes we can, use “ValidationSummary” method from HTML helper class.
<%= Html.ValidationSummary() %>
What are the other data annotation attributes for validation in MVC?
If you want to check string length, you can use “StringLength”.
[StringLength(160)]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
In case you want to use regular expression, you can use “RegularExpression” attribute.
[RegularExpression(@"[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,4}")]public string Email { get; set; }
If you want to check whether the numbers are in range, you can use the “Range” attribute.
[Range(10,25)]public int Age { get; set; }
Some time you would like to compare value of one field with other field, we can use the “Compare” attribute.
public string Password { get; set; }[Compare("Password")]public string ConfirmPass { get; set; }
In case you want to get a particular error message , you can use the “Errors” collection.
var ErrMessage = ModelState["Email"].Errors[0].ErrorMessage;
If you have created the model object yourself you can explicitly call “TryUpdateModel” in your controller to check if the object is valid or not.
TryUpdateModel(NewCustomer);
In case you want add errors in the controller you can use “AddModelError” function.
ModelState.AddModelError("FirstName", "This is my server-side error.");
How can we enable data annotation validation on client side?
It’s a two-step process first reference the necessary jquery files.
<script src="<%= Url.Content("~/Scripts/jquery-1.5.1.js") %>" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="<%= Url.Content("~/Scripts/jquery.validate.js") %>" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="<%= Url.Content("~/Scripts/jquery.validate.unobtrusive.js") %>" type="text/javascript"></script>
Second step is to call “EnableClientValidation” method.
<% Html.EnableClientValidation(); %>
What is razor in MVC?
It’s a light weight view engine. Till MVC we had only one view type i.e.ASPX, Razor was introduced in MVC 3.
Why razor when we already had ASPX?
Razor is clean, lightweight and syntaxes are easy as compared to ASPX. For example in ASPX to display simple time we need to write.
<%=DateTime.Now%>
In Razor it’s just one line of code.
@DateTime.Now
So which is a better fit Razor or ASPX?
As per Microsoft razor is more preferred because it’s light weight and has simple syntaxes.
How can you do authentication and authorization in MVC?
You can use windows or forms authentication for MVC.
How to implement windows authentication for MVC?
For windows authentication you need to go and modify the “web.config” file and set authentication mode to windows.
<authentication mode="Windows"/> <authorization> <deny users="?"/> </authorization>
Then in the controller or on the action you can use the “Authorize” attribute which specifies which users have access to these controllers and actions. Below is the code snippet for the same. Now only the users specified in the controller and action can access the same.
[Authorize(Users= @"WIN-3LI600MWLQN\Administrator")]
public class StartController : Controller
{
//
// GET: /Start/
[Authorize(Users = @"WIN-3LI600MWLQN\Administrator")]
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View("MyView");
}
}
How do you implement forms authentication in MVC?
Forms authentication is implemented the same way as we do in ASP.NET. So the first step is to set authentication mode equal to forms. The “loginUrl” points to a controller here rather than page.
<authentication mode="Forms"> <forms loginUrl="~/Home/Login" timeout="2880"/> </authentication>
We also need to create a controller where we will check the user is proper or not. If the user is proper we will set the cookie value.
public ActionResult Login()
{
if ((Request.Form["txtUserName"] == "Shiv") && (Request.Form["txtPassword"] == "Shiv@123"))
{
FormsAuthentication.SetAuthCookie("Shiv",true);
return View("About");
}
else
{
return View("Index");
}
}
All the other actions need to be attributed with “Authorize” attribute so that any unauthorized user if he makes a call to these controllers it will redirect to the controller ( in this case the controller is “Login”) which will do authentication.
[Authorize]
PublicActionResult Default()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize]
publicActionResult About()
{
return View();
}
How to implement Ajax in MVC?
You can implement Ajax in two ways in MVC: –
- Ajax libraries
- Jquery
Below is a simple sample of how to implement Ajax by using “Ajax” helper library. In the below code you can see we have a simple form which is created by using “Ajax.BeginForm” syntax. This form calls a controller action called as “getCustomer”. So now the submit action click will be an asynchronous ajax call.
<script language="javascript">
function OnSuccess(data1)
{
// Do something here
}
</script>
<div>
<%
var AjaxOpt = new AjaxOptions{OnSuccess="OnSuccess"};
%>
<% using (Ajax.BeginForm("getCustomer","MyAjax",AjaxOpt)) { %>
<input id="txtCustomerCode" type="text" /><br />
<input id="txtCustomerName" type="text" /><br />
<input id="Submit2" type="submit" value="submit"/></div>
<%} %>
In case you want to make ajax calls on hyperlink clicks you can use “Ajax.ActionLink” function as shown in the below code.
Figure:- implement Ajax in MVC
So if you want to create Ajax asynchronous hyperlink by name “GetDate” which calls the “GetDate” function on the controller , below is the code for the same. Once the controller responds this data is displayed in the HTML DIV tag by name “DateDiv”.
<span id="DateDiv" />
<%:
Ajax.ActionLink("Get Date","GetDate",
new AjaxOptions {UpdateTargetId = "DateDiv" })
%>
Below is the controller code. You can see how “GetDate” function has a pause of 10 seconds.
public class Default1Controller : Controller
{
public string GetDate()
{
Thread.Sleep(10000);
return DateTime.Now.ToString();
}
}
The second way of making Ajax call in MVC is by using Jquery. In the below code you can see we are making an ajax POST call to a URL “/MyAjax/getCustomer”. This is done by using “$.post”. All this logic is put in to a function called as “GetData” and you can make a call to the “GetData” function on a button or a hyper link click event as you want.
function GetData()
{
var url = "/MyAjax/getCustomer";
$.post(url, function (data)
{
$("#txtCustomerCode").val(data.CustomerCode);
$("#txtCustomerName").val(data.CustomerName);
}
)
}
What kind of events can be tracked in AJAX?
Figure:- tracked in AJAX
What is the difference between “ActionResult” and “ViewResult”?
“ActionResult” is an abstract class while “ViewResult” derives from “ActionResult” class. “ActionResult” has several derived classes like “ViewResult” ,”JsonResult” , “FileStreamResult” and so on.
“ActionResult” can be used to exploit polymorphism and dynamism. So if you are returning different types of view dynamically “ActionResult” is the best thing. For example in the below code snippet you can see we have a simple action called as “DynamicView”. Depending on the flag (“IsHtmlView”) it will either return “ViewResult” or “JsonResult”.
public ActionResult DynamicView()
{
if (IsHtmlView)
return View(); // returns simple ViewResult
else
return Json(); // returns JsonResult view
}
What are the different types of results in MVC?
Note: -It’s difficult to remember all the 12 types. But some important ones you can remember for the interview are “ActionResult”, “ViewResult” and “JsonResult”. Below is a detailed list for your interest.
There 12 kinds of results in MVC, at the top is “ActionResult”class which is a base class that canhave11subtypes’sas listed below: –
- ViewResult – Renders a specified view to the response stream
- PartialViewResult – Renders a specified partial view to the response stream
- EmptyResult – An empty response is returned
- RedirectResult – Performs an HTTP redirection to a specified URL
- RedirectToRouteResult – Performs an HTTP redirection to a URL that is determined by the routing engine, based on given route data
- JsonResult – Serializes a given ViewData object to JSON format
- JavaScriptResult – Returns a piece of JavaScript code that can be executed on the client
- ContentResult – Writes content to the response stream without requiring a view
- FileContentResult – Returns a file to the client
- FileStreamResult – Returns a file to the client, which is provided by a Stream
- FilePathResult – Returns a file to the client
What are “ActionFilters”in MVC?
“ActionFilters” helps you to perform logic while MVC action is executing or after a MVC action has executed.
Figure:- “ActionFilters”in MVC
Action filters are useful in the following scenarios:-
- Implement post-processinglogicbeforethe action happens.
- Cancel a current execution.
- Inspect the returned value.
- Provide extra data to the action.
You can create action filters by two ways:-
- Inline action filter.
- Creating an “ActionFilter” attribute.
To create a inline action attribute we need to implement “IActionFilter” interface.The “IActionFilter” interface has two methods “OnActionExecuted” and “OnActionExecuting”. We can implement pre-processing logic or cancellation logic in these methods.
public class Default1Controller : Controller , IActionFilter
{
public ActionResult Index(Customer obj)
{
return View(obj);
}
void IActionFilter.OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext filterContext)
{
Trace.WriteLine("Action Executed");
}
void IActionFilter.OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext)
{
Trace.WriteLine("Action is executing");
}
}
The problem with inline action attribute is that it cannot be reused across controllers. So we can convert the inline action filter to an action filter attribute. To create an action filter attribute we need to inherit from “ActionFilterAttribute” and implement “IActionFilter” interface as shown in the below code.
public class MyActionAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute , IActionFilter
{
void IActionFilter.OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext filterContext)
{
Trace.WriteLine("Action Executed");
}
void IActionFilter.OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext)
{
Trace.WriteLine("Action executing");
}
}
Later we can decorate the controllers on which we want the action attribute to execute. You can see in the below code I have decorated the “Default1Controller” with “MyActionAttribute” class which was created in the previous code.
[MyActionAttribute]
public class Default1Controller : Controller
{
public ActionResult Index(Customer obj)
{
return View(obj);
}
}
Can we create our custom view engine using MVC?
Yes, we can create our own custom view engine in MVC. To create our own custom view engine we need to follow 3 steps:-
Let’ say we want to create a custom view engine where in the user can type a command like “<DateTime>” and it should display the current date and time.
Step 1:- We need to create a class which implements “IView” interface. In this class we should write the logic of how the view will be rendered in the “render” function. Below is a simple code snippet for the same.
public class MyCustomView : IView
{
private string _FolderPath; // Define where our views are stored
public string FolderPath
{
get { return _FolderPath; }
set { _FolderPath = value; }
}
public void Render(ViewContext viewContext, System.IO.TextWriter writer)
{
// Parsing logic <dateTime>
// read the view file
string strFileData = File.ReadAllText(_FolderPath);
// we need to and replace <datetime> datetime.now value
string strFinal = strFileData.Replace("<DateTime>", DateTime.Now.ToString());
// this replaced data has to sent for display
writer.Write(strFinal);
}
}
Step 2 :-We need to create a class which inherits from “VirtualPathProviderViewEngine” and in this class we need to provide the folder path and the extension of the view name. For instance for razor the extension is “cshtml” , for aspx the view extension is “.aspx” , so in the same way for our custom view we need to provide an extension. Below is how the code looks like. You can see the “ViewLocationFormats” is set to the “Views” folder and the extension is “.myview”.
public class MyViewEngineProvider : VirtualPathProviderViewEngine
{
// We will create the object of Mycustome view
public MyViewEngineProvider() // constructor
{
// Define the location of the View file
this.ViewLocationFormats = new string[] { "~/Views/{1}/{0}.myview", "~/Views/Shared/{0}.myview" }; //location and extension of our views
}
protected override IView CreateView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewPath, string masterPath)
{
var physicalpath = controllerContext.HttpContext.Server.MapPath(viewPath);
MyCustomView obj = new MyCustomView(); // Custom view engine class
obj.FolderPath = physicalpath; // set the path where the views will be stored
return obj; // returned this view paresing logic so that it can be registered in the view engine collection
}
protected override IView CreatePartialView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string partialPath)
{
var physicalpath = controllerContext.HttpContext.Server.MapPath(partialPath);
MyCustomView obj = new MyCustomView(); // Custom view engine class
obj.FolderPath = physicalpath; // set the path where the views will be stored
return obj; // returned this view paresing logic so that it can be registered in the view engine collection
}
}
Step 3:- We need to register the view in the custom view collection. The best place to register the custom view engine in the “ViewEngines” collection is the “global.asax” file. Below is the code snippet for the same.
protected void Application_Start()
{
// Step3 :- register this object in the view engine collection
ViewEngines.Engines.Add(new MyViewEngineProvider());
<span class="Apple-tab-span" style="white-space: pre; "> </span>…..
}
Below is a simple output of the custom view written using the commands defined at the top.
Figure:-customviewengineusingMVC
If you invoke this view you should see the following output.
How to send result back in JSON format in MVC?
In MVC we have “JsonResult” class by which we can return back data in JSON format. Below is a simple sample code which returns back “Customer” object in JSON format using “JsonResult”.
public JsonResult getCustomer()
{
Customer obj = new Customer();
obj.CustomerCode = "1001";
obj.CustomerName = "Shiv";
return Json(obj,JsonRequestBehavior.AllowGet);
}
Below is the JSON output of the above code if you invoke the action via the browser.
What is “WebAPI”?
HTTP is the most used protocol.For past many years browser was the most preferred client by which we can consume data exposed over HTTP. But as years passed by client variety started spreading out. We had demand to consume data on HTTP from clients like mobile,javascripts,windows application etc.
For satisfying the broad range of client “REST” was the proposed approach. You can read more about “REST” from WCF chapter.
“WebAPI” is the technology by which you can expose data over HTTP following REST principles.
But WCF SOAP also does the same thing, so how does “WebAPI” differ?
| SOAP | WEB API | |
| Size | Heavy weight because of complicated WSDL structure. | Light weight, only the necessary information is transferred. |
| Protocol | Independent of protocols. | Only for HTTP protocol |
| Formats | To parse SOAP message, the client needs to understand WSDL format. Writing custom code for parsing WSDL is a heavy duty task. If your client is smart enough to create proxy objects like how we have in .NET (add reference) then SOAP is easier to consume and call. | Output of “WebAPI” are simple string message,JSON,Simple XML format etc. So writing parsing logic for the same in very easy. |
| Principles | SOAP follows WS-* specification. | WEB API follows REST principles. (Please refer about REST in WCF chapter). |
With WCF also you can implement REST,So why “WebAPI”?
WCF was brought in to implement SOA, never the intention was to implement REST.”WebAPI'” is built from scratch and the only goal is to create HTTP services using REST. Due to the one point focus for creating “REST” service “WebAPI” is more preferred.
How to implement “WebAPI” in MVC?
Below are the steps to implement “webAPI” :-
Step1:-Create the project using the “WebAPI” template.
Figure:- implement “WebAPI” in MVC
Step 2:- Once you have created the project you will notice that the controller now inherits from “ApiController” and you can now implement “post”,”get”,”put” and “delete” methods of HTTP protocol.
public class ValuesController : ApiController
{
// GET api/values
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
// GET api/values/5
public string Get(int id)
{
return "value";
}
// POST api/values
public void Post([FromBody]string value)
{
}
// PUT api/values/5
public void Put(int id, [FromBody]string value)
{
}
// DELETE api/values/5
public void Delete(int id)
{
}
}
Step 3:-If you make a HTTP GET call you should get the below results.
Figure:- HTTP
Finally do not forget to visit my video site which covers lots of C# interview questions and answers: –www.questpond.com
from:http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/556995/Model-view-controller-MVC-Interview-questions-and
250+ SQL Queries Interview Question Answers
This is a never ending topic and there is no limit to questions that all depends on profile and interviewer.
I am trying my level best to divide questionnaire based on Experience in Query Writing skills
- 5+ Years of Experience (Expert)
- 2-5 Years of Experience (Intermediate)
- 1-2 Years of Experience (Beginner)
- Fresher to 1 years of Experience (Fresher)
SQL Queries Interview Questions for Experts (5-10 Years of experience)
Suppose, you are build a application like FACEBOOK and as a business you need to suggest Friend by displaying Friends of Friend’s. So you need to build a query that should return resultset which should have Friend Friend name. Just for reference, this is how friend table looks like,
create table Friend
(
ProfileID uniqueidentifier,
Name varchar(50),
Friend_Name varchar(50)
)
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'RAM', 'Shyam')
insert Friend values ('FFCB96AD-0F16-4A77-B634-3CE1F697A3D1','RAM', 'Tony')
insert Friend values ('FFCB96AD-0F16-4A77-B634-3CE1F697A3D1','RAM', 'Vibha')
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'SHYAM', 'RAM')
insert Friend values ('42A6A0EC-8EE5-4611-92C7-A23B0970B463','SHYAM', 'SAM')
insert Friend values ('42A6A0EC-8EE5-4611-92C7-A23B0970B463','SHYAM', 'Vibha')
insert Friend values ('42A6A0EC-8EE5-4611-92C7-A23B0970B463','SHYAM', 'John')
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'VIBHA', 'RAM')
insert Friend values ('AC40284F-4E54-495A-BF62-9701474C44C0','VIBHA', 'SHYAM')
insert Friend values ('AC40284F-4E54-495A-BF62-9701474C44C0','VIBHA', 'George')
insert Friend values ('AC40284F-4E54-495A-BF62-9701474C44C0','VIBHA', 'TOM')
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'TOM', 'RAM')
insert Friend values ('DE86E5EC-9748-47A0-936E-0BB6BCBCA1A0','TOM', 'DNATAG')
insert Friend values ('DE86E5EC-9748-47A0-936E-0BB6BCBCA1A0','TOM', 'Reddy')
Solution
-- Query Solution
declare @user varchar(50)
set @user = 'RAM'
SELECT f1.name,
f2.friend_name as friend_of_friend
FROM friend f1,
friend f2
WHERE f1.name = @user
AND f1.friend_name = f2.name
AND NOT EXISTS
(SELECT 1 FROM friend f3
WHERE f3.name = f1.name
AND f3.friend_name = f2.friend_name) and f2.friend_name <>@user
What is blocking and how would you troubleshoot it?
Blocking happens when one connection from an application holds a lock and a second connection requires a conflicting lock type. This forces the second connection to wait, blocked on the first.
What are the steps you will take to improve performance of a poor performing query?
This is a very open ended question and there could be a lot of reasons behind the poor performance of a query. But some general issues that you could talk about would be: No indexes, table scans, missing or out of date statistics, blocking, excess recompilations of stored procedures, procedures and triggers without SET NOCOUNT ON, poorly written query with unnecessarily complicated joins, too much normalization, excess usage of cursors and temporary tables.
Some of the tools/ways that help you troubleshooting performance problems are:
- SET SHOWPLAN_ALL ON,
- SET SHOWPLAN_TEXT ON,
- SET STATISTICS IO ON,
- SQL Server Profiler,
- Windows NT /2000 Performance monitor,
- Graphical execution plan in Query Analyzer.
You are being you being assigned a task to move 5 million rows from one server to another using T-SQL with a linked-server. What will you consider to avoid transaction log fill up at destination server?
Will prefer to use SET ROWCOUNT and a while loop to commit data in batches.
What is the optimal Disk configuration for a database server and what RAID configurations would you use if budget is not a constraint?
- RAID 1 for the OS / Applications
- RAID 1 for the page file
- RAID 10 for the Data file (or RAID 5 for few writes)
- RAID 1 (or 10) for the transaction log
What is a deadlock and what is a live lock? How will you go about resolving deadlocks?
Deadlock is a situation when two processes, each having a lock on one piece of data, attempt to acquire a lock on the other’s piece. Each process would wait indefinitely for the other to release the lock, unless one of the user processes is terminated. SQL Server detects deadlocks and terminates one user’s process.
A livelock is one, where a request for an exclusive lock is repeatedly denied because a series of overlapping shared locks keeps interfering. SQL Server detects the situation after four denials and refuses further shared locks. A livelock also occurs when read transactions monopolize a table or page, forcing a write transaction to wait indefinitely.
Check out SET DEADLOCK_PRIORITY and “Minimizing Deadlocks” in SQL Server books online. Also check out the article Q169960 from Microsoft knowledge base.
What is blocking and how would you troubleshoot it?
Blocking happens when one connection from an application holds a lock and a second connection requires a conflicting lock type. This forces the second connection to wait, blocked on the first.
Read up the following topics in SQL Server books online: Understanding and avoiding blocking, Coding efficient transactions.
What are statistics, under what circumstances they go out of date, how do you update them?
Statistics determine the selectivity of the indexes. If an indexed column has unique values then the selectivity of that index is more, as opposed to an index with non-unique values. Query optimizer uses these indexes in determining whether to choose an index or not while executing a query.
Some situations under which you should update statistics:
- If there is significant change in the key values in the index
- If a large amount of data in an indexed column has been added, changed, or removed (that is, if the distribution of key values has changed), or the table has been truncated using the TRUNCATE TABLE statement and then repopulated
- Database is upgraded from a previous version
Look up SQL Server books online for the following commands:
UPDATE STATISTICS,
STATS_DATE,DBCC SHOW_STATISTICS,
CREATE STATISTICS,
DROP STATISTICS,
sp_autostats,
sp_createstats,
sp_updatestats
Write SQL query to find the products which have continuous increase in sales every year considering the following Schema and tell which optimized query?
Table Structure
CREATE TABLE PRODUCTS
(
PRODUCT_ID INTEGER,
PRODUCT_NAME VARCHAR(30)
);
CREATE TABLE SALES
(
SALE_ID INTEGER,
PRODUCT_ID INTEGER,
YEAR INTEGER,
Quantity INTEGER,
PRICE INTEGER
);
This table, contains the following rows,
Solution
SELECT PRODUCT_NAME
FROM
(
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME,
S.QUANTITY -
LEAD(S.QUANTITY,1,0) OVER (
PARTITION BY P.PRODUCT_ID
ORDER BY S.YEAR DESC
) QUAN_DIFF
FROM PRODUCTS P,
SALES S
WHERE P.PRODUCT_ID = S.PRODUCT_ID
)A
GROUP BY PRODUCT_NAME
HAVING MIN(QUAN_DIFF) >= 0;
Note – This Solution is using a LEAD fn, which is available in SQL Server 2012.
Based on above mentioned tables, Write two alternative SQL query to find the products which does not have sales at all and identify, which is more optimized.
-- OPTION 1
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME
FROM PRODUCTS P
LEFT OUTER JOIN
SALES S
ON (P.PRODUCT_ID = S.PRODUCT_ID)
WHERE S.QUANTITY IS NULL
-- OPTION 2
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME
FROM PRODUCTS P
WHERE P.PRODUCT_ID NOT IN
(SELECT DISTINCT PRODUCT_ID FROM SALES);
-- Option 3
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME
FROM PRODUCTS P
WHERE NOT EXISTS
(SELECT 1 FROM SALES S WHERE S.PRODUCT_ID = P.PRODUCT_ID);
Based on above mentioned tables,Write two alternatives query to select the top product sold in each year?
-- OPTION 1
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME,
S.YEAR,
S.QUANTITY
FROM
(
SELECT YEAR,
MAX(QUANTITY) QUAN
FROM SALES
GROUP BY YEAR
)A, SALES S,
PRODUCTS P
WHERE A.YEAR = S.YEAR
AND A.QUAN = S.QUANTITY
AND S.PRODUCT_ID = P.PRODUCT_ID;
-- Option 2
SELECT PRODUCT_NAME,
YEAR
FROM
(
SELECT P.PRODUCT_NAME,
S.YEAR,
RANK() OVER (
PARTITION BY S.YEAR
ORDER BY S.QUANTITY DESC
) RNK
FROM PRODUCTS P,
SALES S
WHERE P.PRODUCT_ID = S.PRODUCT_ID
) A
WHERE RNK = 1;
OUTPUT
Based on above mentioned tables structure, Write a query to find the products whose quantity sold in a year should be greater than the average quantity sold across all the years??
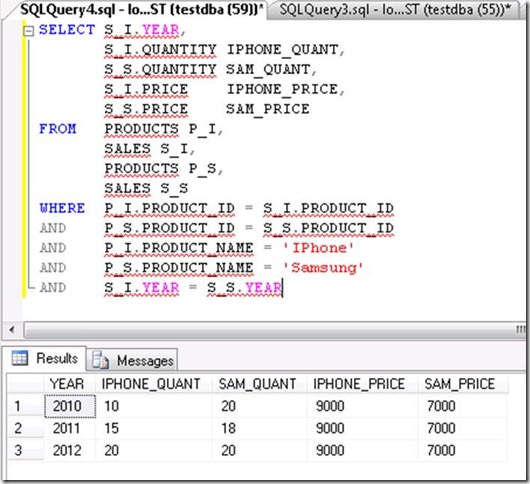
Based on above mentioned tables structure, Write a query to compare the products sales of “IPhone” and “Samsung” in each year?
Could you please some items which you may see in an execution plan indicating the query
is not optimized.
- Index Scan or Table Scan
- Hash Joins
- Thick arrows (indicating large work tables)
- Parallel streams (Parallelism)
- Bookmark lookup (or key lookup)
What structure can you implement for the database to speed up table reads?
Follow the rules of DB tuning we have to:
1] properly use indexes ( different types of indexes)
2] properly locate different DB objects across different tablespaces, files and so on.
3] create a special space (tablespace) to locate some of the data with special datatype ( for example CLOB, LOB and …)
SQL Queries Interview Questions for Intermediate (2-5 Years of experience)
What is Lock Escalation?
Lock escalation is the process of converting a lot of low level locks (like row locks, page locks) into higher level locks (like table locks). Every lock is a memory structure too many locks would mean, more memory being occupied by locks. To prevent this from happening, SQL Server escalates the many fine-grain locks to fewer coarse-grain locks. Lock escalation threshold was definable in SQL Server 6.5, but from SQL Server 7.0 onwards it’s dynamically managed by SQL Server.
What is a bookmark lookup?
When a non clustered index is used for the seek and the data needed was not
at the leaf level.
What is a key lookup?
Same as bookmark lookup, when a non clustered index is used for the seek and the data needed was not
at the leaf level.
What new indexes are introduced in SQL Server onwards ?
– Spatial
– XML
Could you please describe some properties / Facts about NULL during comparisons.
NULL can not used with any comparing operator, NULL
- NULL will never be true or false
- NULL can not compared as =,<>,<,>, <=,<= etc.
- NILL is always equates will NULL only
What are cursors? Explain different types of cursors. What are the disadvantages of cursors? How can you avoid cursors?
Cursors allow row-by-row processing of the resultsets.
Types of cursors:
Static,
Dynamic,Forward-only,
Keyset-driven.
See books online for more information.
Disadvantages of cursors: Because we know cursor doing roundtrip it will make network line busy and also make time consuming methods. First of all select query gernate output and after that cursor goes one by one so roundtrip happen.Another disadvange of cursor are ther are too costly because they require lot of resources and temporary storage so network is quite busy. Moreover, there are restrictions on SELECT statements that can be used with some types of cursors.
Most of the times, set based operations can be used instead of cursors. Here is an example:
If you have to give a flat hike to your employees using the following criteria:
Salary between 30000 and 40000 — 5000 hike
Salary between 40000 and 55000 — 7000 hikeSalary between 55000 and 65000 — 9000 hike
In this situation many developers tend to use a cursor, determine each employee’s salary and update his salary according to the above formula. But the same can be achieved by multiple update statements or can be combined in a single UPDATE statement as shown below:
UPDATE tbl_emp SET salary =
CASE WHEN salary BETWEEN 30000 AND 40000 THEN salary + 5000WHEN salary BETWEEN 40000 AND 55000 THEN salary + 7000
WHEN salary BETWEEN 55000 AND 65000 THEN salary + 10000
END
Another situation in which developers tend to use cursors: You need to call a stored procedure when a column in a particular row meets certain condition. You don’t have to use cursors for this. This can be achieved using WHILEloop, as long as there is a unique key to identify each row.
Could you please explain, how to use Cursors ?
- Declare a CURSOR
- OPEN a CURSOR
- FETCH data in CURSOR
- finally close CURSOR
Suppose, we are building a UAT environment and we need to build a algorithm to export exact 50% of the rows (I means to say alternative rows either even or ODD). So write a query to select prime number rows from table.
select profileid,name,friend_name
from (select f.*, row_number() over (order by profileid asc) rn
from Friend f) a
where rn%2=1;
Testing Script
create table Friend
(
ProfileID uniqueidentifier,
Name varchar(50),
Friend_Name varchar(50)
)
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'RAM', 'Shyam')
insert Friend values ('FFCB96AD-0F16-4A77-B634-3CE1F697A3D1','RAM', 'Tony')
insert Friend values ('FFCB96AD-0F16-4A77-B634-3CE1F697A3D1','RAM', 'Vibha')
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'SHYAM', 'RAM')
insert Friend values ('42A6A0EC-8EE5-4611-92C7-A23B0970B463','SHYAM', 'SAM')
insert Friend values ('42A6A0EC-8EE5-4611-92C7-A23B0970B463','SHYAM', 'Vibha')
insert Friend values ('42A6A0EC-8EE5-4611-92C7-A23B0970B463','SHYAM', 'John')
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'VIBHA', 'RAM')
insert Friend values ('AC40284F-4E54-495A-BF62-9701474C44C0','VIBHA', 'SHYAM')
insert Friend values ('AC40284F-4E54-495A-BF62-9701474C44C0','VIBHA', 'George')
insert Friend values ('AC40284F-4E54-495A-BF62-9701474C44C0','VIBHA', 'TOM')
insert Friend values (NEWid(),'TOM', 'RAM')
insert Friend values ('DE86E5EC-9748-47A0-936E-0BB6BCBCA1A0','TOM', 'DNATAG')
insert Friend values ('DE86E5EC-9748-47A0-936E-0BB6BCBCA1A0','TOM', 'Reddy')
go
select profileid,name,friend_name
from (select e.*, row_number() over (order by profileid asc) rn
from Friend e) a
where rn%2=1;
What is the system function to get the current user’s user id?
USER_ID(). Also check out other system functions like
USER_NAME(),
SYSTEM_USER,SESSION_USER,
CURRENT_USER,
USER,
SUSER_SID(),
HOST_NAME().
What is precedence constraints and can you name some?
Precedence constraints are used in DTS / SSIS packages to move from one
task to another. We have three type of precedence constraints
- Success
- Failure
- Completion
What sort of resource contention we can have, which can cause database to run slow?
- CPU bottleneck
- Memory bottleneck
- Network IO bottleneck
- Disk IO bottleneck
- Paging File (process trimming)
- Lock contention
- Corrupt index
- Recompilation
Can you have a nested transaction?
Yes, SQL Server do support nested transaction up to 32 levels. Check out BEGIN TRAN, COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVE TRAN and @@TRANCOUNT
Which is faster a Table Scan, or a Clustered Index Scan?
Same speed in case a table has a clustered index that it’s always show index scan instead of table scan.
What is an extended stored procedure? Can you instantiate a COM object by using T-SQL?
An extended stored procedure is a function within a DLL (written in a programming language like C, C++ using Open Data Services (ODS) API) that can be called from T-SQL, just the way we call normal stored procedures using theEXEC statement. See books online to learn how to create extended stored procedures and how to add them to SQL Server.
Yes, you can instantiate a COM (written in languages like VB, VC++) object from T-SQL by using sp_OACreatestored procedure.
Also see books online for sp_OAMethod, sp_OAGetProperty, sp_OASetProperty, sp_OADestroy.
What is recompilation?
When the cached execution plan for a query cannot be used so the procedure
recompiles.
What is parallelism?
SQL Server can perform a query or index operation in parallel by using several operating system threads, the operation can be completed quickly. When a single query runs of multiple CPUs is known as query parallelism.
What is the default query threshold for parallelism?
The query optimizer decides to utilize multiple SPIDS running on different processors to query / transfer data. Default threshold is 5 seconds.
What are the main reasons for statement recompilation ?
Recompilation happen mainly because of
- underlying statistics change
- DDL changes within the procedure.
- The parameters the procedure was compiled with vary from the recently passed in parameters.
- The query plan was flushed from cache.
How will you handle exceptions in SQL Server programming
By using TRY-CATCH constructs,
What is difference between Co-related sub query and nested sub query?
Correlated subquery runs once for each row selected by the outer query. It contains a reference to a value from the row selected by the outer query.
Nested subquery runs only once for the entire nesting (outer) query. It does not contain any reference to the outer query row.
For example,
Correlated Subquery:
select e1.empname, e1.basicsal, e1.deptno from emp e1 where e1.basicsal = (select max(basicsal) from emp e2 where e2.deptno = e1.deptno)
Nested Subquery:
select empname, basicsal, deptno from emp where (deptno, basicsal) in (select deptno, max(basicsal) from emp group by deptno)
Let’s assume, you are working for online product selling company like AMAZON, now you need to write two alternatives query to return the firstname, lastname and the most recent OrderID for all customers.
-- OPTION 1 SELECT o.OrderID,c.FirstName,c.LastName FROM Orders o JOIN Customers c ON o.CustomerID = c.CustomerID WHERE OrderDate = (SELECT MAX(OrderDate) FROM Orders WHERE CustomerID = o.CustomerID -- OPTION 2 SELECT c.FirstName,c.LastName,o.OrderNumber FROM Orders o JOIN ( SELECT MAX(OrderDate) AS MaxOrderDate, custid FROM orders GROUP BY custid ) o_2 ON o.custid = o_2.custid AND o.orderdate = o_2.MaxOrderDate JOIN customers c ON c.CustID = o.CustID
What tools do you use for performance tuning?
Query Analyzer, Profiler, Index Wizard, Performance Monitor
What are extended stored procedures?
How can you execute a DOS command from SQL or through SQL query by using xp_cmdshell?
exec xp_cmdshell 'dir c:\*.exe'
What sp_MSforeachtable does ?
You can use sp_MSforeachtable undocumented stored procedure to rebuild all indexes in your database. Try to schedule it to execute during CPU idle time and slow production periods.
sp_MSforeachtable @command1=”print ‘?’ DBCC DBREINDEX (‘?’)”
How do I prevent SQL injection in my applications?
Check my previous post, “How to secure against SQL injection“.
What you do when a particular query is slow?
- Run SQL profiler and determine if abnormal amounts of IO or CPU is used.
- Run profiler to determine if recompilation is a factor.
- Update the statistics.
- Check the execution plan
Can we convert the column datatype in to different datatype in a exiting table ?
YES, we can change data type of column for an exiting table too but we need to make sure the new datatype is compateble with old datatype. For Example, we can not convert a column which store varchar values and has textual data in it to a int type data type. Following TSQL can be used to modify (alter) a exiting column
alter table tablename alter Column Columnname newdatatype
SQL Queries Interview Questions for Beginner (1-2 Years of experience)
In what sequence SQL statement are processed?
The clauses of the select are processed in the following sequence
- FROM clause
- WHERE clause
- GROUP BY clause
- HAVING clause
- SELECT clause
- ORDER BY clause
- TOP clause
Can we write a distributed query and get some data which is located on other server and on Oracle Database ?
SQL Server can be lined to any server provided it has OLE-DB provider from Microsoft to allow a link.
E.g. Oracle has a OLE-DB provider for oracle that Microsoft provides to add it as linked server to SQL Server group.
If we drop a table, does it also drop related objects like constraints, indexes, columns, defaults, Views and Stored Procedures ?
YES, SQL Server drops all related objects, which exists inside a table like, constraints, indexes, columns, defaults etc. BUT dropping a table will not drop Views and Stored Procedures as they exists outside the table.
How would you determine the time zone under which a database was operating?
Can we add identity column to decimal datatype?
YES, SQL Server support this
What is the Difference between LEFT JOIN with WHERE clause & LEFT JOIN with no WHERE clause ?
OUTER LEFT/RIGHT JOIN with WHERE clause can act like an INNER JOIN if not used wisely or logically.
What are the Multiple ways to execute a dynamic query ?
EXEC sp_executesql, EXECUTE()
What is the Difference between COALESCE() & ISNULL() ?
ISNULL accepts only 2 parameters. The first parameter is checked for NULL value, if it is NULL then the second parameter is returned, otherwise it returns first parameter.
COALESCE accepts two or more parameters. One can apply 2 or as many parameters, but it returns only the first non NULL parameter,
How do you generate file output from SQL?
While using SQL Server Management Studio or Query Analyzer, we have an option in Menu BAR.QUERTY >> RESULT TO >> Result to FILE
How do you prevent SQL Server from giving you informational messages during and after a SQL statement execution?
SET NOCOUNT OFF
By Mistake, Duplicate records exists in a table, how can we delete copy of a record ?
;with T as
(
select * , row_number() over (partition by Emp_ID order by Emp_ID) as rank
from employee
)
delete
from T
where rank > 1
WHAT OPERATOR PERFORMS PATTERN MATCHING?
Pattern matching operator is LIKE and it has to used with two attributes
1. % means matches zero or more characters and
2. _ ( underscore ) means matching exactly one character
What’s the logical difference, if any, between the following SQL expressions?
-- Statement 1 SELECT COUNT ( * ) FROM Employees -- Statement 2 SELECT SUM ( 1 ) FROM Employees
They’re the same unless table Employee table is empty, in which case the first yields a one-column, one-row table containing a zero and the second yields a one-column, one-row table “containing a null.”
Is it possible to update Views? If yes, How, If Not, Why?
Yes, We can modify views but a DML statement on a join view can modify only one base table of the view (so even if the view is created upon a join of many tables, only one table, the key preserved table can be modified through the view).
Could you please name different kinds of Joins available in SQL Server ?
- OUTER JOIN – LEFT, RIGHT, CROSS, FULL ;
- INNER JOIN
How important do you consider cursors or while loops for a transactional database?
would like to avoid cursor in OLTP database as much as possible, Cursors are mainly only used for maintenance or warehouse operations.
What is a correlated sub query?
When a sub query is tied to the outer query. Mostly used in self joins.
What is faster, a correlated sub query or an inner join?
Correlated sub query.
You are supposed to work on SQL optimization and given a choice which one runs faster, a correlated sub query or an exists?
Exists
Can we call .DLL from SQL server?
YES, We can call .Dll from SQL Server. Please check my previous post, “How to call a .dll file in SQL Server”
What are the pros and cons of putting a scalar function in a queries select list or in the where clause?
Should be avoided if possible as Scalar functions in these places make the query slow down dramatically.
What is difference between truncate and drop statement ?
Check my previous post difference between TRUNCATE & DELETE
What is difference between truncate and delete statement ?
Check my previous post difference between TRUNCATE & DELETE
What are user defined data types and when you should go for them?
User defined data types let you extend the base SQL Server data types by providing a descriptive name, and format to the database. Take for example, in your database, there is a column called Flight_Num which appears in many tables. In all these tables it should be varchar(8). In this case you could create a user defined data type calledFlight_num_type of varchar(8) and use it across all your tables.
See sp_addtype, sp_droptype in books online.
Can You Explain Integration Between SQL Server 2005 And Visual Studio 2005 ?
This integration provide wider range of development with the help of CLR for database server because CLR helps developers to get flexibility for developing database applications and also provides language interoperability just like Visual C++, Visual Basic .Net and Visual C# .Net. The CLR helps developers to get the arrays, classes and exception handling available through programming languages such as Visual C++ or Visual C# which is use in stored procedures, functions and triggers for creating database application dynamically and also provide more efficient reuse of code and faster execution of complex tasks. We particularly liked the error-checking powers of the CLR environment, which reduces run-time errors
Please check my previous post, “Can we call .DLL from SQL server?”
You are being assigned to create a complex View and you have completed that task and that view is ready to be get pushed to production server now. you are supposed to fill a deployment form before any change is pushed to production server.
One of the Filed in that deployment form asked, “Expected Storage requirement”. What all factors you will consider to calculate storage requirement for that view ?
Very tricky, View, doesn’t takes space in Database, Views are virtual tables. Storage is required to store Index, incase you are developing a indexed view.
What is Index, cluster index and non cluster index ?
Clustered Index:- A Clustered index is a special type of index that reorders the way records in the table are physically stored. Therefore table may have only one clustered index.Non-Clustered Index:- A Non-Clustered index is a special type of index in which the logical order of the index does not match the physical stored order of the rows in the disk. The leaf nodes of a non-clustered index does not consists of the data pages. instead the leaf node contains index rows.
Write down the general syntax for a SELECT statements covering all the options.
Here’s the basic syntax: (Also checkout SELECT in books online for advanced syntax).
SELECT select_list
[INTO new_table_]FROM table_source
[WHERE search_condition]
[GROUP BY group_by__expression]
[HAVING search_condition]
[ORDER BY order__expression [ASC | DESC] ]
What is a join and explain different types of joins?
Joins are used in queries to explain how different tables are related. Joins also let you select data from a table depending upon data from another table.
Types of joins:
INNER JOINs,
OUTER JOINs,CROSS JOINs
OUTER JOINs are further classified as
LEFT OUTER JOINS,
RIGHT OUTER JOINS andFULL OUTER JOINS.
For more information see pages from books online titled: “Join Fundamentals” and “Using Joins“.
What is OSQL utility ?
OSQL is command line tool which is used execute query and display the result same a query analyzer but everything is in command prompt.
What Is Difference Between OSQL And Query Analyzer ?
OSQL is command line tool which executes query and display the result same a query analyzer but query analyzer is graphical and OSQL is a command line tool. OSQL is quite useful for batch processing or executing remote queries.
What Is Cascade delete / update ?
CASCADE allows deletions or updates of key values to cascade through the tables defined to have foreign key relationships that can be traced back to the table on which the modification is performed.
What is a self join? Explain it with an example.
Self join is just like any other join, except that two instances of the same table will be joined in the query. Here is an example: Employees table which contains rows for normal employees as well as managers. So, to find out the managers of all the employees, you need a self join.
CREATE TABLE emp
(empid int,
mgrid int,
empname char(10)
)
INSERT emp SELECT 1,2,’Vyas’
INSERT emp SELECT 2,3,’Mohan’INSERT emp SELECT 3,NULL,’Shobha’
INSERT emp SELECT 4,2,’Shridhar’
INSERT emp SELECT 5,2,’Sourabh’
SELECT t1.empname [Employee], t2.empname [Manager]
FROM emp t1, emp t2WHERE t1.mgrid = t2.empid
Here is an advanced query using a LEFT OUTER JOIN that even returns the employees without managers (super bosses)
SELECT t1.empname [Employee], COALESCE(t2.empname, ‘No manager’) [Manager]
FROM emp t1LEFT OUTER JOIN
emp t2
ON
t1.mgrid = t2.empid
What are some of the join algorithms used when SQL Server joins tables.
- Loop Join (indexed keys unordered)
- Merge Join (indexed keys ordered)
- Hash Join (non-indexed keys)
What is maximum number of tables that can joins in a single query ?
256, check SQL Server Limits
What is Magic Tables in SQL Server ?
The MAGIC tables are automatically created and dropped, in case you use TRIGGERS. SQL Server has two magic tables named, INSERTED and DELETED
These are mantained by SQL server for there Internal processing. When we use update insert or delete on tables these magic tables are used.These are not physical tables but are Internal tables.When ever we use insert statement is fired the Inserted table is populated with newly inserted Row and when ever delete statement is fired the Deleted table is populated with the delete
d row.But in case of update statement is fired both Inserted and Deleted table used for records the Original row before updation get store in Deleted table and new row Updated get store in Inserted table.
Can we disable a triger?, if yes HOW ?
YES, we can disable a single trigger on the database by using “DISABLE TRIGGER triggerName ON <<TableName>>”
we also have an option to disable all the trigger by using, “DISABLE Trigger ALL ON ALL SERVER”
Why you need indexing? where that is Stored and what you mean by schema object? For what purpose we are using view?
We can’t create an Index on Index.. Index is stoed in user_index table. Every object that has been created on Schema is Schema Object like Table, View etc. If we want to share the particular data to various users we have to use the virtual table for the Base table. So that is a view.
Indexing is used for faster search or to retrieve data faster from various table. Schema containing set of tables, basically schema means logical separation of the database. View is crated for faster retrieval of data. It’s customized virtual table. we can create a single view of multiple tables. Only the drawback is..view needs to be get refreshed for retrieving updated data.
What the difference between UNION and UNIONALL?
Union will remove the duplicate rows from the result set while Union all does’nt.
Which system table contains information on constraints on all the tables created ?
USER_CONSTRAINTS,
system table contains information on constraints on all the tables created
What are different Types of Join?
- Cross Join A cross join that does not have a WHERE clause produces the Cartesian product of the tables involved in the join. The size of a Cartesian product result set is the number of rows in the first table multiplied by the number of rows in the second table. The common example is when company wants to combine each product with a pricing table to analyze each product at each price.
- Inner Join A join that displays only the rows that have a match in both joined tables is known as inner Join. This is the default type of join in the Query and View Designer.
- Outer JoinA join that includes rows even if they do not have related rows in the joined table is an Outer Join. You can create three different outer join to specify the unmatched rows to be included:
- Left Outer Join: In Left Outer Join all rows in the first-named table i.e. “left” table, which appears leftmost in the JOIN clause are included. Unmatched rows in the right table do not appear.
- Right Outer Join: In Right Outer Join all rows in the second-named table i.e. “right” table, which appears rightmost in the JOIN clause are included. Unmatched rows in the left table are not included.
- Full Outer Join: In Full Outer Join all rows in all joined tables are included, whether they are matched or not.
- Self Join This is a particular case when one table joins to itself, with one or two aliases to avoid confusion. A self join can be of any type, as long as the joined tables are the same. A self join is rather unique in that it involves a relationship with only one table. The common example is when company has a hierarchal reporting structure whereby one member of staff reports to another. Self Join can be Outer Join or Inner Join.
What is Data-Warehousing?
- Subject-oriented, meaning that the data in the database is organized so that all the data elements relating to the same real-world event or object are linked together;
- Time-variant, meaning that the changes to the data in the database are tracked and recorded so that reports can be produced showing changes over time;
- Non-volatile, meaning that data in the database is never over-written or deleted, once committed, the data is static, read-only, but retained for future reporting.
- Integrated, meaning that the database contains data from most or all of an organization’s operational applications, and that this data is made consistent.
What is a live lock?
A live lock is one, where a request for an exclusive lock is repeatedly denied because a series of overlapping shared locks keeps interfering. SQL Server detects the situation after four denials and refuses further shared locks. A live lock also occurs when read transactions monopolize a table or page, forcing a write transaction to wait indefinitely.
How SQL Server executes a statement with nested subqueries?
When SQL Server executes a statement with nested subqueries, it always executes the innermost query first. This query passes its results to the next query and so on until it reaches the outermost query. It is the outermost query that returns a result set.
How do you add a column to a existing table?
ALTER TABLE Department ADD (AGE, NUMBER);
Can one drop a column from a table?
YES, to delete a column in a table, use ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name
Which statement do you use to eliminate padded spaces between the month and day values in a function TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,’Month, DD, YYYY’) ?
To remove padded spaces, you use the “fm” prefix before the date element that contains the spaces. TO_CHAR(SYSDATE,’fmMonth DD, YYYY’)
Which operator do you use to return all of the rows from one query except rows are returned in a second query?
You use the EXCEPT operator to return all rows from one query except where duplicate rows are found in a second query. The UNION operator returns all rows from both queries minus duplicates. The UNION ALL operator returns all rows from both queries including duplicates. The INTERSECT operator returns only those rows that exist in both queries. Check my previous post, “How to use EXCEPT Operator” for learn more.
How you will create a column alias?
The AS keyword is optional when specifying a column alias.
In what sequence SQL statement are processed?
The clauses of the subselect are processed in the following sequence (DB2): 1. FROM clause 2. WHERE clause 3. GROUP BY clause 4. HAVING clause 5. SELECT clause 6. ORDER BY clause 7. FETCH FIRST clause
How can we determine what objects a user-defined function depends upon?
sp_depends system stored procedure or query the sysdepends system table to return a list of objects that a user-defined function depends upon
SELECT DISTINCT so1.name, so2.name FROM sysobjects so1 INNER JOIN sysdepends sd ON so1.id = sd.id INNER JOIN sysobjects so2 ON so2.id = sd.depid WHERE so1.name = '<<OBJECT_NAME>>'
What is lock escalation ?
A query first takes the lowest level lock possible with the smallest footprint (row-level). When too many rows are locked (requiring too much RAM) the lock is escalated to a range or page lock. If too many pages are locked, it may escalate to a table lock.
What are the main differences between #temp tables and @table variables and which one is preferred ?
- SQL Server can create column statistics on #temp tables
- Indexes can be created on #temp tables
- @table variables are stored in memory up to a certain threshold.
For many other question and more information on temporary table and variable, check my previous post.
What are Checkpoint In SQL Server ?
When we done operation on SQL SERVER that is not commited directly to the database.All operation must be logged in to Transaction Log files after that they should be done on to the main database.CheckPoint are the point which alert Sql Server to save all the data to main database if no check point is there then log files get full we can use Checkpoint command to commit all data in the SQL SERVER.When we stop the SQL Server it will take long time because Checkpoint is also fired.
Why we use OPENXML clause?
OPENXML parses the XML data in SQL Server in an efficient manner. It’s primary ability is to insert XML data to the DB.
Can we store we store PDF files inside SQL Server table ?
YES, we can store this sort of data using a blob datatype.
Can we store Videos inside SQL Server table ?
YES, we can store Videos inside SQL Server by using FILESTREAM datatype, which was introduced in SQL Server 2008.
Can we hide the definition of a stored procedure from a user ?
YES, while creating stored procedure we can use WITH ENCRYPTION which will convert the original text of the CREATE PROCEDURE statement to an encrypted format.
What are included columns when we talk about SQL Server indexing?
Indexed with included columns were developed in SQL Server 2005 that assists in covering queries. Indexes with Included Columns are non clustered indexes that
have the following benefits:
- Columns defined in the include statement, called non-key columns, are not counted in the
number of columns by the Database Engine. - Columns that previously could not be used in queries, like nvarchar(max), can be included
as a non-key column. - A maximum of 1023 additional columns can be used as non-key columns.
What is an execution plan? How would you view the execution plan?
An execution plan is basically a road map that graphically or textually shows the data retrieval methods chosen by the SQL Server query optimizer for a stored procedure or ad-hoc query and is a very useful tool for a developer to understand the performance characteristics of a query or stored procedure since the plan is the one that SQL Server will place in its cache and use to execute the stored procedure or query. From within Query Analyzer is an option called “Show Execution Plan” (located on the Query drop-down menu). If this option is turned on it will display query execution plan in separate window when query is ran again.
Explain UNION, MINUS, UNION ALL, INTERSECT ?
INTERSECT returns all distinct rows selected by both queries.
MINUS – returns all distinct rows selected by the first query but not by the second.
UNION – returns all distinct rows selected by either query
UNION ALL – returns all rows selected by either query, including all duplicates
What is ROWID ?
SQL Queries Interview Questions for Fresher’s (Starters)
How to find second highest value of a column in a table?
-- Option 1 SELECT max(SAL) FROM EMP WHERE SAL < ( SELECT max(SAL) FROM EMP); -- Option 2 SELECT max( SAL) FROM EMP WHERE SAL NOT IN( SELECT max(SAL) FROM EMP ); -- Option 3 SELECT max(value1) FROM ( SELECT value1 FROM val EXCEPT SELECT max(value1) FROM val ); -- Option 4 SELECT * FROM EMP WHERE SAL IN (SELECT MAX(SAL) FROM EMP WHERE SAL <> (SELECT MAX(SAL) FROM EMP))
What is the difference between DDL and DML commands? Can you name some examples of each?
DDL Statements are data definition language commands. Examples are CREATE,
ALTER and DROP. where as DML Statements are data manipulation language commands. Examples are INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE.
What are the advantages of using Views ?
- Views restrict access to the data because the view can display selective columns from the table.
- Views provide data independence for ad hoc users and application programs. One view can be used to retrieve data from several tables.
- Views provide groups of users access to data according to their particular criteria.
- Views provides an additional level of table security, by restricting access to a predetermined set of rows and columns of a table.
- Hide data complexity.
- Simplify commands for the user.
- Present the data in a different perpecetive from that of the base table.
- Store complex queries.
What is query optimization?
Query optimization is the part of the query process in which the database system compares different query strategies and chooses the one with the least expected cost
What are the main components of Database management systems software.
The database management system software includes components for storage management, concurrency control, transaction processing, database manipulation interface, database definition interface, and database control interface.
What is transaction?
A transaction is a collection of applications code and database manipulation code bound into an indivisible unit of execution. it consists from: BEGIN-TRANSACTION Name Code END TRANSACTION Name
What is schema?
A schema is collection of database objects of a Use.
How to find structure of an existing table ?
What is difference between alias and synonym ?
Alias is a temporary used with in a query but Synonyms are permanent in a database.
Are Views automatically updated, when we insert / update the base table ?
YES, Views always displays the updated data and there is no need to manually update them. Views doesn’t store any data they refer base table for data.
What is the difference between a “where” clause and a “having” clause?
“Where” is a kind of restiriction statement. You use where clause to restrict all the data from DB.Where clause is using before result retrieving. But Having clause is using after retrieving the data.Having clause is a kind of filtering command.
Can you name some other alternatives to SQL Server ?
Informix, Oracle, DB2, MySQL
What is the basic form of a SQL statement to read data out of a table?
The basic form to read data out of table is ‘SELECT * FROM table_name; ‘ An answer: ‘SELECT * FROM table_name WHERE xyz= ‘whatever’;’ cannot be called basic form because of WHERE clause.
What structure can you implement for the database to speed up table reads?
Follow the rules of DB tuning we have to: 1] properly use indexes ( different types of indexes) 2] properly locate different DB objects across different tablespaces, files and so on.3] create a special space (tablespace) to locate some of the data with special datatype ( for example CLOB, LOB and …)
What are the tradeoffs with having indexes?
1. Faster selects, slower updates. 2. Extra storage space to store indexes. Updates are slower because in addition to updating the table you have to update the index.
What is a “join”?
Join used to connect two or more tables logically with or without common field.
What is normalization? “Denormalization”? Why do we sometimes want to denormalize?
Normalizing data means eliminating redundant information from a table and organizing the data so that future changes to the table are easier. Denormalization means allowing redundancy in a table. The main benefit of denormalization is improved performance with simplified data retrieval and manipulation. This is done by reduction in the number of joins needed for data processing.
What is a “constraint”?
A constraint allows you to apply simple referential integrity checks to a table. There are four primary types of constraints that are currently supported by SQL Server: PRIMARY/UNIQUE – enforces uniqueness of a particular table column. DEFAULT – specifies a default value for a column in case an insert operation does not provide one. FOREIGN KEY – validates that every value in a column exists in a column of another table. CHECK – checks that every value stored in a column is in some specified list. Each type of constraint performs a specific type of action. Default is not a constraint. NOT NULL is one more constraint which does not allow values in the specific column to be null. And also it the only constraint which is not a table level constraint.
What types of index data structures can you have?
An index helps to faster search values in tables. The three most commonly used index-types are: – B-Tree: builds a tree of possible values with a list of row IDs that have the leaf value. Needs a lot of space and is the default index type for most databases. – Bitmap: string of bits for each possible value of the column. Each bit string has one bit for each row. Needs only few space and is very fast.(however, domain of value cannot be large, e.g. SEX(m,f); degree(BS,MS,PHD) – Hash: A hashing algorithm is used to assign a set of characters to represent a text string such as a composite of keys or partial keys, and compresses the underlying data. Takes longer to build and is supported by relatively few databases.
What is a “primary key”?
A PRIMARY INDEX or PRIMARY KEY is something which comes mainly from
database theory. From its behavior is almost the same as an UNIQUE INDEX, i.e. there may only be one of each value in this column. If you call such an INDEX PRIMARY instead of UNIQUE, you say something about
your table design, which I am not able to explain in few words. Primary Key is a type of a constraint enforcing uniqueness and data integrity for each row of a table. All columns participating in a primary key constraint must possess the NOT NULL property.
What is a “functional dependency”? How does it relate to database table design?
Functional dependency relates to how one object depends upon the other in the database. for example, procedure/function sp2 may be called by procedure sp1. Then we say that sp1 has functional dependency on sp2.
What is a “trigger”?
Triggers are stored procedures created in order to enforce integrity rules in a database. A trigger is executed every time a data-modification operation occurs (i.e., insert, update or delete). Triggers are executed automatically on occurance of one of the data-modification operations. A trigger is a database object directly associated with a particular table. It fires whenever a specific statement/type of statement is issued against that table. The types of statements are insert,update,delete and query statements. Basically, trigger is a set of SQL statements A trigger is a solution to the restrictions of a constraint. For instance: 1.A database column cannot carry PSEUDO columns as criteria where a trigger can. 2. A database constraint cannot refer old and new values for a row where a trigger can.
What is “index covering” of a query?
Index covering means that “Data can be found only using indexes, without touching the tables”
What types of join algorithms can you have?
What is a SQL view?
An output of a query can be stored as a view. View acts like small table which meets our criterion. View is a precomplied SQL query which is used to select data from one or more tables. A view is like a table but it doesn’t physically take any space. View is a good way to present data in a particular format if you use that query quite often. View can also be used to restrict users from accessing the tables directly.
How do you implement one-to-one, one-to-many and many-to-many relationships while designing tables?
One-to-One relationship can be implemented as a single table and rarely as two tables with primary and foreign key relationships. One-to-Many relationships are implemented by splitting the data into two tables with primary key and foreign key relationships. Many-to-Many relationships are implemented using a junction table with the keys from both the tables forming the composite primary key of the junction table. It will be a good idea to read up a database designing fundamentals text book.
What’s the difference between a primary key and a unique key?
Both primary key and unique enforce uniqueness of the column on which they are defined. But by default primary key creates a clustered index on the column, where are unique creates a non-clustered index by default. Another major difference is that, primary key does not allow NULLs, but unique key allows one NULL only.
What is bit data type and what’s the information that can be stored inside a bit column?
Bit data type is used to store Boolean information like 1 or 0 (true or false). Until SQL Server 6.5 bit data type could hold either a 1 or 0 and there was no support for NULL. But from SQL Server 7.0 onwards, bit data type can represent a third state, which is NULL
Define candidate key, alternate key, composite key.
A candidate key is one that can identify each row of a table uniquely. Generally a candidate key becomes the primary key of the table. If the table has more than one candidate key, one of them will become the primary key, and the rest are called alternate keys.
A key formed by combining at least two or more columns is called composite key.
What are defaults? Is there a column to which a default cannot be bound?
A default is a value that will be used by a column, if no value is supplied to that column while inserting data.IDENTITY columns and timestamp columns can’t have defaults bound to them. See CREATE DEFAULT in books online.
What is a transaction and what are ACID properties?
A transaction is a logical unit of work in which, all the steps must be performed or none. ACID stands for Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability. These are the properties of a transaction. For more information and explanation of these properties, see SQL Server books online or any RDBMS fundamentals text book.
Explain different isolation levels
An isolation level determines the degree of isolation of data between concurrent transactions. The default SQL Server isolation level is Read Committed. Here are the other isolation levels (in the ascending order of isolation): Read Uncommitted, Read Committed, Repeatable Read, Serializable. See SQL Server books online for an explanation of the isolation levels. Be sure to read about SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL, which lets you customize the isolation level at the connection level.
CREATE INDEX myIndex ON myTable (myColumn)
What type of Index will get created after executing the above statement?
Non-clustered index. Important thing to note: By default a clustered index gets created on the primary key, unless specified otherwise.
What is the maximum size of a row?
8060 bytes. Do not be surprised with questions like ‘What is the maximum number of columns per table’. Check out SQL Server books online for the page titled: “Maximum Capacity Specifications”.
What are constraints? Explain different types of constraints.
Constraints enable the RDBMS enforce the integrity of the database automatically, without needing you to create triggers, rule or defaults.
Types of constraints: NOT NULL, CHECK, UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY
For an explanation of these constraints see books online for the pages titled: “Constraints” and “CREATE TABLE”, “ALTER TABLE”
What is an index? What are the types of indexes? How many clustered indexes can be created on a table? I create a separate index on each column of a table. what are the advantages and disadvantages of this approach?
Indexes in SQL Server are similar to the indexes in books. They help SQL Server retrieve the data quicker.
- Indexes are of two types. Clustered indexes and non-clustered indexes. When you create a clustered index on a table, all the rows in the table are stored in the order of the clustered index key. So, there can be only one clustered index per table. Non-clustered indexes have their own storage separate from the table data storage. Non-clustered indexes are stored as B-tree structures (so do clustered indexes), with the leaf level nodes having the index key and it’s row locater. The row located could be the RID or the Clustered index key, depending up on the absence or presence of clustered index on the table.If you create an index on each column of a table, it improves the query performance, as the query optimizer can choose from all the existing indexes to come up with an efficient execution plan. At the same time, data modification operations (such as INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) will become slow, as every time data changes in the table, all the indexes need to be updated. Another disadvantage is that, indexes need disk space, the more indexes you have, more disk space is used.
What are triggers? How many triggers you can have on a table? How to invoke a trigger on demand?
Triggers are special kind of stored procedures that get executed automatically when an INSERT, UPDATE or DELETEoperation takes place on a table.
In SQL Server 6.5 you could define only 3 triggers per table, one for INSERT, one for UPDATE and one for DELETE. From SQL Server 7.0 onwards, this restriction is gone, and you could create multiple triggers per each action. But in 7.0 there’s no way to control the order in which the triggers fire. In SQL Server 2000 you could specify which trigger fires first or fires last using sp_settriggerorder
Triggers cannot be invoked on demand. They get triggered only when an associated action (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) happens on the table on which they are defined.
Triggers are generally used to implement business rules, auditing. Triggers can also be used to extend the referential integrity checks, but wherever possible, use constraints for this purpose, instead of triggers, as constraints are much faster.
Till SQL Server 7.0, triggers fire only after the data modification operation happens. So in a way, they are called post triggers. But in SQL Server 2000 you could create pre triggers also. Search SQL Server 2000 books online forINSTEAD OF triggers.
Also check out books online for ‘inserted table’, ‘deleted table’ and COLUMNS_UPDATED()
There is a trigger defined for INSERT operations on a table, in an OLTP system. The trigger is written to instantiate a COM object and pass the newly inserted rows to it for some custom processing.
What is the difference between oracle, sql and sql server ?
- Oracle is based on RDBMS.
- SQL is Structured Query Language.
- SQL Server is another tool for RDBMS provided by MicroSoft.
Difference between Stored Procedure and Trigger?
- we can call stored procedure explicitly.
- but trigger is automatically invoked when the action defined in trigger is done.
ex: create trigger after Insert on - this trigger invoked after we insert something on that table.
- Stored procedure can’t be inactive but trigger can be Inactive.
- Triggers are used to initiate a particular activity after fulfilling certain condition.It need to define and can be enable and disable according to need.
What is the advantage to use trigger in your PL?
A trigger is a database object directly associated with a particular table. It fires whenever a specific statement/type of statement is issued against that table. The types of statements are insert,update,delete and query statements. Basically, trigger is a set of SQL statements A trigger is a solution to the restrictions of a constraint. For instance: 1.A database column cannot carry PSEUDO columns as criteria where a trigger can. 2. A database constraint cannot refer old and new values for a row where a trigger can.
Triggers are fired implicitly on the tables/views on which they are created. There are various advantages of using a trigger. Some of them are:
- Suppose we need to validate a DML statement(insert/Update/Delete) that modifies a table then we can write a trigger on the table that gets fired implicitly whenever DML statement is executed on that table.
- Another reason of using triggers can be for automatic updation of one or more tables whenever a DML/DDL statement is executed for the table on which the trigger is created.
- Triggers can be used to enforce constraints. For eg : Any insert/update/ Delete statements should not be allowed on a particular table after office hours. For enforcing this constraint Triggers should be used.
- Triggers can be used to publish information about database events to subscribers. Database event can be a system event like Database startup or shutdown or it can be a user even like User loggin in or user logoff.
What is a SQL view?
An output of a query can be stored as a view. View acts like small table which meets our criterion. View is a pre-complied SQL query which is used to select data from one or more tables. A view is like a table but it doesn’t physically take any space. View is a good way to present data in a particular format if you use that query quite often. View can also be used to restrict users from accessing the tables directly.
The GROUP BY keywords has been added to SQL because aggregate functions (like SUM) return the aggregate of all column values every time they are called. Without the GROUP BY functionality, finding the sum for each individual group of column values was not possible.
What are defaults? Is there a column to which a default can’t be bound?
A default is a value that will be used by a column, if no value is supplied to that column while inserting data. IDENTITY columns and timestamp columns can’t have defaults bound to them.
What does COMMIT do?
Saving all changes made by DML statements
List all the possible values that can be stored in a BOOLEAN data field.
There are only two values that can be stored in a BOOLEAN data field: -1(true) and 0(false).
What is the highest value that can be stored in a BYTE data field?
The highest value that can be stored in a BYTE field is 255. or from -128 to 127.
Explain SQL SELECT example:
select j.FILE_NUM from DB_name.job j, DB_name.address a where j.JOB_TYPE ='C' AND j.COMPANY_NAME = 'TEST6' AND j.OFFICE_ID = '101' AND j.ACTIVE_IND = 'Y' AND a.ADDRESS_STATUS_ID = 'H' AND a.OFFICE_ID = '101' AND a.FILE_NUM = j.FILE_NUM order by j.FILE_NUM;
J and A are aliases for table names. this is outer join select statement from two tables.
Describe some Group Functions that you know
- The COUNT function tells you how many rows were in the result set. SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Employees
- The AVG function tells you the average value of a numeric column. SELECT MAX(SALARY) FROM Employees
- The MAX and MIN functions tell you the maximum and minimum value of a numeric column. SELECT MIN(SALARY) FROM Employees
- The SUM function tells you the sum value of a numeric column. SELECT SUM(SALARY) FROM Employees
What does DML stand for? DML is Data Manipulation Language statements. (SELECT)
What does DDL stand for?
DDL is Data Definition Language statements. (CREATE)
What does DCL stand for?
DCL is Data Control Language statements. (COMMIT)
What is SQL comments and how to inser comments in SQL statements?
SQL comments are introduced by two consecutive hyphens (–) and ended by the end of the line.
What is the difference between a return parameter and an OUTPUT parameter?
A return parameter is always returned by a stored procedure,and it is meant to indicate the success or failure of the stored procedure. The return parameter is always an INT data type.
An OUTPUT parameter is designated specifically by the developer, and it can return other types of data, such as characters and numeric values.
You can use multiple OUTPUT parameters in a stored procedure,whereas you can only use one return parameter.
What is the minimum number of tables required to perform a SQL join?
One, you can join a table as a self join too, consider an example of employee table which has a column EMPID, NAME and Mgr ID and we need to display EMPID, name of the employee and MGRID of that employee,
How can present Summarizing Data in SQL Server?
CUBE or ROLLUP operators to generate summary reports. Both are part of the GROUP BY Clause
What is Service Broker
Its a message queuing technology in SQL to helps developer to develop fully ditributed applications.Its helps to send asynchronous, transactional message.Its also helps to send message to another database.
What is SQL Profiler
SQL Profiler is a graphical tool thats helps administrator to capture events in instance of Microsoft Sql Server. We can get all the events that done on file or on SQL Table.We can filter the events that we need for us.We can also get the subset of event that we need.Why not to use prefix sp in store procedure
Thses prefix is used by master database so SQL server first searches in the master database and then in the current session database. So its time taken is much higher master database causes extra overhead and also get wrong result in case of same name in master database.What is the advantage of SET NOCOUNT ON
When we use SELECT and DML statement in SQL .SQL server return a message which specify the number of rows effected by these statements. This information helps coder when they are debugging the code other wise this is not useful we can disable this by typing SET NOCOUNT ON. It is very helpful when we are doing on store procedure contains lots of statements,loops its also increase in performance and boost network traffic.Why to use SQL Sequence and its drawbacks
In SQL Sequences are used for creating sequence numbers without any overhead of locking but one drawback is that when any of transaction is rolled back the sequence number is lost.What are the different ways of moving data from database
There are different methods of moving data- BACKUP and RESTORE
- detach and attach
- Attaching databases
- Replication
- DTS
- BCP
- logshipping
- INSERT…SELECT
- SELECT…INTO
- SQL Server 2012 HADR
- creating INSERT scripts to generate data.
How to get top two records without Top keyword
set rowcount 2select column,column1 from tblEmployeeMaster
What do you mean by KEYSET Cursor
KEYSET Cursor uses the set of keys that are primary key or we can saw uniquely identify the cursor’s rows. SQL Server uses a table in tempdb to store keyset. The KEYSET cursor helps to updates non key values from being made through this cursor, but when inserts made by other users are not visible. Updates nonkey values made by other users are visible as the owner scrolls around the cursor, but updates key values made by other users are not visible.
Difference between Set and Select
- Set is a ANSI standard for variable assignment.
- Select is a Non-ANSI standard when assigning variables.
- Set – We can assign only one variable at a time
- Select – We can assign multiple variable at a time
When assigning from a query that returns more than one value, SET will fail with an error.
When assigning from a query that returns more than one value, SELECT will assign the last value returned by the query and hide the fact that the query returnedWhat is Network Packet Size in SQL
NPS(Network Packet Size) is the size of the TDS (tabular data stream) packets used to communicate between your applications and your relational database engine and default packet size is 4 kilobytes and its manily depends on network packet size configuration option.
What are Sparse Columns in Sql Server2008
Sparse column is a tool that helps to reduce amount of physical storage used in a database. These are ordinary columns that have an optimized storage for all null values.SPARSE column are better at managing NULL and ZERO values in SQL Server. It does not take any space in database at all.
Can we create non primary key as cluster index
Yes we can do this on non-primary key column but that column must be unique and the primary key column of that table must have non-clustered index because there is one cluster index in table. By default primary key column contains clustered index so its recommended to create such non-primary key clustered index column first and then should create primary key column so in such case the primary key on that column will be with non-clustered. But its highly recommended to create primary key column as a clustered indexed column.Could you please give some Optimization Tips in writing SQL Queries ?
- Always try to use views and stored procedures instead of doing work with heavy queries.
- Make a habit to use constraints instead of triggers whenever it is possible.
- When you need n number of row from database try to use top keyword or SET ROWCOUNT statement
- Always use table variables in place of temporary tables.
- Avoid Union and try to use UNION ALL statement.
- Always avoid using the DISTINCT clause, whenever possible.
- Always try to avoid using SQL Server cursors.
- Always try to avoid the HAVING clause.
- Do not use select count(*) to get number of rows
- Try to include SET NOCOUNT ON statement into your stored procedures to stop the message indicating the number of rows affected by a T-SQL statement.
- Always use file system to store large binary objects and use the file path in database.
- Sometimes we may have to apply more than one sub queries in our main query. Try to minimize the number of sub query block in your query.
- Try to use column name instead of *
Why Group BY and Order By clause are so expensive
These both of these requires Temporary table to process the result of query so these are expensiveWhat is the default value of int datatype
The default value of all datatype is NULL
Is it possible to create foreign key without primary key
Yes we can do this by the help of Unique Key constraint . Means table must have atleast Primary key or Unique key.
Does SQL Server supports Merge statement ?
YES, This is newly introduced feature in SQL Server 2008
What is Trace frag in SQL
The Trace Tags is used to set temporary setting of specific server characteristics. DBCC TRACEON is the command to set the trace flags. Once activated, trace flag will be in effect until the server is restarted. Trace frags are frequently used for diagnosing performance issues.For example, the trace flag 3205 is used for disabling hard compression for tape drives, when an instance of SQL Server starts.
What is Pivot and Unpivot
We can sort, count, and total the data stored in one table or spreadsheet and create a second table displaying the summarized data with the Pivot tables. The PIVOT operator turns the values of a specified column into column names, effectively rotating a table.
UNPIVOT table is reverse of PIVOT Table.Can we call a Trigger in store procedure
A Trigger is also a special kind of Stored Procedure which will fire automatically on the happening of an event like before or after insert, update or delete. We cannot call a trigger explicitly from a Stored Procedure.
Why we use SET ROWCOUNT in Sql
This syntax is used in SQL Server to stop processing the query after the specified number of rows are returned.
Why we use Unicode In Sql server
Unicode data is stored using the nchar, nvarchar,and ntext data types in SQL Server. Use these data types for columns that store characters from more than one character set. The SQL Server Unicode data types are based on the National Character data types in the SQL-92 standard.What is SQL Cache Dependency in ASP.NET 2.0
SQL cache dependencies is new technique in ASP.NET 2.0 which can automatically invalidate a cached data object just like a Dataset. when the related data is modified in the database. So for instance if you have a dataset which is tied up to a database tables any changes in the database table will invalidate the cached data object which can be a dataset or a data source.To enable this we need a syntax that is as follows:- aspnet_regsql -ed -E -d Northwindfrom:http://www.sqlserver-training.com/250-sql-queries-interview-question-answers/–
potentially a huge advantage in league of item team fights
Support plays a lot of bonus content such as champion and late game you That’s not winning your ap damage matters the entire game where league of legends laners are equally trading and even learn about everything that’s included in losing a 1v1 This can prepare yourself to gain access to single handily carry You’ll never struggle on top against your opponents in coming out on one box This can enable you already know Ranked Boost hasn’t missed any patch release If you’ve followed us on Youtube then you That’s not just champion select You’ll be able to face off against any patch release If you’ve